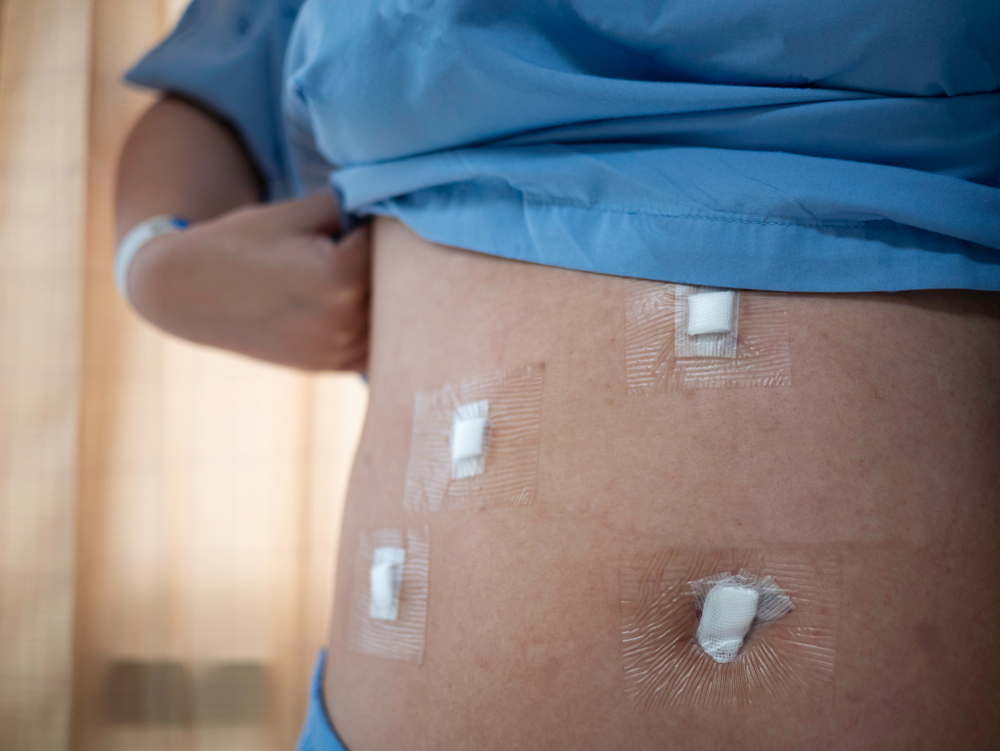
October 9, 2024
Post-operative wound healing is a crucial aspect of recovery after any surgery, impacting both the speed of healing and overall patient outcomes. To ensure optimal recovery, understand the best practices for surgical wound care and the different phases of healing.
Key takeaways for effective post-operative wound healing:
– Keep wounds clean: Prevent infections by maintaining strict hygiene.
– Support wound healing: Use appropriate dressings and follow healthcare guidelines.
– Understand healing phases: Familiarize yourself with the inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling stages.
We will explore the intricate phases of wound healing, from inflammation to remodeling, and provide actionable tips for optimal surgical wound care. Understanding these phases can help healthcare professionals and patients alike to steer the healing journey more effectively, ultimately improving recovery experiences and outcomes.

Understanding the Phases of Wound Healing
When it comes to post-operative wound healing, understanding the stages your body goes through can make a big difference. Let’s break down the three main phases: inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling.
Inflammatory Phase
This is the body’s immediate response to injury. Right after surgery, your body jumps into action. Blood vessels around the wound expand, increasing blood flow. This might make the area look red and feel warm. This extra blood brings in neutrophils and macrophages, which are like the body’s clean-up crew. They help fight off bacteria and clear out dead tissue.

You’ll notice signs of inflammation: redness, heat, swelling, and maybe some pain. These are all normal parts of the inflammatory phase. It’s your body’s way of starting the healing process.
Proliferative Phase
Next, we move into the proliferative phase. This is where the wound really starts to rebuild. New tissue, called granulation tissue, forms. It’s made of collagen and other important substances that fill in the wound.
You’ll also see new blood vessels forming, a process known as angiogenesis. This helps bring nutrients to the healing area. The wound edges start to pull together and shrink, and new skin begins to cover the wound.
Remodeling Phase
Finally, we reach the remodeling phase. This phase can last for months. During this time, the new tissue strengthens and matures. Collagen fibers reorganize, making the wound area stronger.
The wound might look like it’s healed on the outside, but inside, the body is still working hard. Over time, the wound area will regain most of its original strength. The blood supply to the area will also return to normal.
Understanding these phases can help you support your body’s natural healing process. Each phase is crucial for ensuring that your wound heals properly and efficiently. By recognizing the signs and stages of healing, you can better manage your recovery and achieve the best possible outcomes.
Essential Post-Operative Wound Care Tips
Proper care of your surgical wound is key to healing well and avoiding infections. Let’s explore some essential tips for post-operative wound healing.
Proper Handwashing Techniques
Clean hands are your first line of defense against infection. Always wash your hands before touching your wound or changing your dressing.
Here’s how to do it right:
- Remove jewelry from your hands.
- Wet your hands with warm water.
- Apply soap and scrub for 15 to 30 seconds. You can sing “Happy Birthday” to time it.
- Clean under your nails too.
- Rinse well and dry with a clean towel.
If soap and water aren’t available, an alcohol-based cleanser is a good alternative.
How to Change Your Dressing
Changing your dressing keeps your wound clean and promotes healing. Follow these steps for a smooth process:
- Gather your supplies: Make sure everything you need is within reach.
- Wash your hands thoroughly.
- Remove the old dressing: Loosen the tape gently. If it sticks, dampen it to ease removal.
- Dispose of the old dressing in a plastic bag.
- Wash your hands again before applying the new dressing.
- Apply the new dressing: Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions. Ensure it sticks well and covers the wound completely.
Different types of dressings serve different purposes. Your healthcare provider will guide you on the best choice for your wound.
Keeping Your Wound Clean
Keeping your wound clean is crucial for preventing infections. Here’s how to do it safely:
- Use saline solution or mild soapy water for cleaning.
- Avoid harsh cleansers like alcohol, peroxide, or iodine—they can damage tissue and slow healing.
- Gently dab or wipe the area with a gauze pad soaked in the solution.
- Pat dry with a clean, soft cloth.
Avoid lotions or creams unless your provider says it’s okay. Keeping the wound clean and dry is the best way to support healing.
By following these simple steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of infection and support your body’s natural healing process. Up next, we’ll explore how nutrition and lifestyle choices can further improve your recovery.
Promoting Faster Healing After Surgery
Nutrition and lifestyle play a crucial role in post-operative wound healing. What you eat and how you live can significantly impact your recovery speed and overall outcome.
Nutritional Support for Healing
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can help your body repair itself faster. Let’s break down some key nutrients:
- Vitamin B12: This vitamin is vital for red blood cell production and tissue repair. Foods like fish, meat, and dairy are excellent sources.
- Iron: Iron supports oxygen transport in the blood, which is crucial for wound healing. Include lean meats, beans, and spinach in your meals.
- Fiber: High-fiber foods like whole grains and vegetables aid digestion and help prevent constipation, a common post-surgery issue.
- Probiotics: These beneficial bacteria, found in yogurt and fermented foods, support gut health and can boost your immune system.
Eating a varied diet with these nutrients can make a big difference in how quickly you heal. Consider talking to a nutritionist if you need personalized advice.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Healing
A few lifestyle adjustments can also improve your recovery. Here’s what to focus on:
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking reduces oxygen flow to your tissues, which slows down healing. Quitting—even temporarily—can improve your recovery.
- Reducing Alcohol Intake: Alcohol can impair your immune system and increase the risk of post-op complications. Cutting back is a smart move for faster healing.
- Exercise Limitations: While some movement is good for circulation, avoid strenuous activities that could strain your wound. Follow your doctor’s advice on when and how to resume exercise.
These changes not only aid in post-operative wound healing but also contribute to overall health and well-being. Making these adjustments can lead to a smoother recovery process.
Next, we’ll discuss how to manage common post-operative complications and what signs to watch for.
Managing Common Post-Operative Complications
After surgery, complications can arise that may hinder your recovery. Knowing what to look for and how to address these issues is key to ensuring a smooth healing process.
Identifying and Treating Infections
Infections are a common post-operative complication. Early detection can prevent serious issues. Here are signs to watch for:
- Redness and Swelling: Some redness and swelling are normal, but if these increase significantly, it could indicate an infection.
- Pus or Discharge: A thick, yellow, or green discharge that smells bad is a red flag. This is often pus, a sign that your body is fighting an infection.
- Fever: A temperature above 100°F (37.7°C) persisting for more than 4 hours could mean an infection.
If you notice any of these signs, contact your healthcare provider immediately. They might prescribe antibiotics or recommend other treatments based on the infection’s severity and type.
Handling Wound Dehiscence
Wound dehiscence, or the reopening of a surgical wound, can be alarming. It usually requires prompt medical attention. Here’s what to know:
- Causes: It can be caused by infection, excessive strain on the wound, or poor nutrition.
- Secondary Healing: If your wound reopens, it may need to heal by secondary intention. This means it will heal from the bottom up and may take longer.
- Medical Intervention: Your doctor might clean the wound, remove any dead tissue, and possibly re-suture it. Follow-up care is crucial to prevent further complications.
Scar Tissue Management
Scar tissue forms as your wound heals. While it’s a natural part of healing, managing its appearance can be important for many.
- Reducing Visibility: Keeping the wound moisturized and protected can help reduce scar formation. Products like silicone gel sheets may also help.
- Sun Protection: Newly healed skin is sensitive to the sun. Use sunscreen or cover the area to prevent discoloration and protect the scar.
By understanding these common complications and how to address them, you can take proactive steps in your recovery journey. Next, we’ll answer some frequently asked questions about post-operative wound healing.
Frequently Asked Questions about Post-Operative Wound Healing
How long does it take for a post-op wound to heal?
The healing time for a post-operative wound can vary widely. It often depends on factors like your general health, the type of surgery you had, and how well you follow your doctor’s care instructions.
- General Health: Individuals in good health tend to heal faster. Conditions like diabetes or immune disorders can slow down the process.
- Surgery Type: Minor surgeries may see wounds heal in a couple of weeks, while more extensive procedures might take months. For instance, a simple skin incision may heal in about two weeks, whereas a more complex abdominal surgery could take six weeks or more.
What are the signs of an infected wound?
Infections can hinder healing and cause complications. Here are some signs of an infection you should watch for:
- Pain: Increasing pain at the site of the wound can signal infection.
- Redness and Swelling: While some redness and swelling are normal, an increase in these symptoms could indicate a problem.
- Pus: The presence of pus or a foul-smelling discharge is a strong indicator of infection.
If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately. Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent further complications.
How can I promote wound healing after surgery?
Promoting healing involves a combination of good nutrition, lifestyle changes, and proper wound care.
- Nutrition: Eating foods rich in vitamins and minerals, like B12 and iron, supports healing. Probiotics and fiber can also be beneficial.
- Lifestyle Changes: Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake, as both can slow down the healing process.
- Wound Care: Keep your wound clean and dry, and follow your doctor’s instructions for changing dressings. Avoid using harsh cleansers that could irritate the wound.
By understanding these aspects of post-operative wound healing, you can take proactive steps to ensure a smooth and speedy recovery.
Conclusion
At Gladiator Therapeutics, LLC, we understand the importance of post-operative wound healing in ensuring a smooth recovery. Our innovative SemiCera® Technology is designed to improve this process by utilizing non-powered far infrared (FIR) technology. This approach not only accelerates wound healing but also promotes stem cell proliferation, offering a unique solution for patients and healthcare providers alike.
SemiCera® Technology stands out by providing a non-invasive method to improve patient outcomes. Unlike traditional treatments that may rely on medications or powered devices, our technology harnesses the natural benefits of FIR to support the body’s healing processes. This can lead to faster recovery times and reduced risk of complications, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions that typically slow healing, such as diabetes or compromised immune systems.
One of the key advantages of our technology is its potential to reduce treatment costs. Patients may require fewer follow-up visits and less intensive care by promoting faster healing, ultimately lowering healthcare expenses. This cost-effectiveness, combined with the ease of use of our devices, makes SemiCera® an appealing option for both patients and medical professionals.
We are committed to advancing wound care and improving quality of life for those with challenging medical needs. Our dedication to research and innovation ensures that we continue to develop effective solutions that meet the evolving demands of the healthcare industry.
For more information on our products and how they can benefit post-operative recovery, visit our Gladiator Therapeutics product page. Find how our technology can play a vital role in supporting your healing journey.
- Tags:
- age healing